Diarrhea in puppies is much more common than you might think and often causes worry and discomfort for pet owners. Understanding the potential causes behind this type of gastrointestinal upset is pivotal in ensuring proper care and timely intervention for our furry companions.
Younger dogs, with their curious and developing nature, are particularly susceptible to various triggers that can lead to diarrhea. Factors such as dietary changes, food intolerances,  and indiscriminate eating habits can upset their delicate digestive systems, resulting in loose stools and discomfort.
and indiscriminate eating habits can upset their delicate digestive systems, resulting in loose stools and discomfort.
Fortunately, Dr. Smith has seen TONS of diarrhea throughout his career, and he knows just how to handle it. Listen to our diarrhea expert describe the two main causes of diarrhea in puppies in this youtube video. We’ll discuss these causes in detail in the following sections, so come back here right after you watch the video.
In this exploration, we delve into the primary causes of diarrhea in puppies, shedding light on the underlying factors that contribute to this common ailment. By unraveling these causes, dog owners like you can better recognize and address these issues, providing optimal care and seeking appropriate veterinary guidance when necessary to ensure the well-being and health of your younger canine friends.
Parasitic Infection Leading to Diarrhea in Puppies
Parasitic infections pose a significant threat to the gastrointestinal health of younger dogs, often leading to diarrhea and other related symptoms. Seeking prompt veterinary attention, conducting routine fecal tests, and following deworming schedules are crucial in preventing and managing parasitic infections, and minimizing the risk of diarrhea and associated complications in younger dogs.
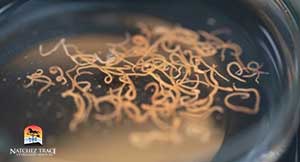 Roundworms (Toxocara spp.):
Roundworms (Toxocara spp.):
- Common in puppies, roundworms can cause diarrhea, vomiting, and a potbellied appearance. They’re transmitted through the ingestion of infected feces or through contaminated environments.
- Whipworms (Trichuris vulpis):
- Whipworms affect the large intestine, causing chronic diarrhea, weight loss, and anemia. Dogs contract whipworms by ingesting infected soil or feces.
- Giardia (Giardia spp.):
- Giardiasis causes watery diarrhea, vomiting, and weight loss. Dogs become infected by ingesting water or food contaminated with the parasite.
- Coccidia (Coccidia spp.):
- Coccidiosis leads to diarrhea, dehydration, and occasionally bloody stools. Transmission occurs through contact with infected feces or soil.
- Hookworms (Ancylostoma spp. and Uncinaria spp.):
- Hookworm infestations lead to bloody diarrhea, anemia, and weakness. Dogs contract hookworms through skin contact or ingestion of larvae in contaminated environments.
Indiscriminate Eating Causes Diarrhea in Dogs
Understanding the potential risks associated with indiscriminate eating enables pet owners to implement preventive measures, ensuring a safer environment and reducing the likelihood of dog diarrhea stemming from ingestion of inappropriate or harmful substances by younger dogs.
 Curiosity and Exploration:
Curiosity and Exploration:
- Younger dogs, driven by curiosity and a natural inclination to explore their surroundings, often resort to indiscriminate eating. They may ingest non-food items, garbage, or outdoor debris.
- Potential Hazards:
- Consuming non-edible substances can lead to gastrointestinal irritation or blockages, triggering diarrhea. Common items ingested include rocks, plastic, plants, or spoiled food.
- Behavioral Concerns:
- Indiscriminate eating can stem from behavioral issues like anxiety, boredom, or attention-seeking behavior, prompting dogs to ingest unfamiliar or inappropriate items.
- Health Risks:
- Ingesting foreign objects or toxic substances may cause severe digestive distress, leading to diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or, in severe cases, intestinal obstructions requiring immediate veterinary care.
- Preventive Measures:
- Training and supervision play pivotal roles in curbing this behavior. Providing ample physical and mental stimulation, using deterrents for hazardous items, and teaching “leave it” commands can help prevent indiscriminate eating.
Dietary Factors Resulting in Dog Diarrhea
Recognizing the factors listed below is crucial in maintaining a healthy digestive system for younger dogs. Proper vet care, regular deworming, providing a balanced diet, and keeping potentially harmful substances out of reach can significantly reduce the incidence of canine diarrhea caused by these factors.
- Abrupt Diet Changes:
- Younger dogs possess sensitive digestive systems. Abrupt shifts in their diet, such as sudden changes in food brands or types, can disrupt their digestive balance, resulting in diarrhea.
- Food Intolerances or Allergies:
- Some younger dogs may develop sensitivities to certain ingredients in their diet, triggering allergic reactions or intolerances that manifest as diarrhea. Common culprits include grains, certain proteins, or additives in commercial foods.
 Ingestion of Inappropriate Substances:
Ingestion of Inappropriate Substances:
- Curiosity often leads younger dogs to indiscriminately eat items they encounter. Consuming non-food items, garbage, or plants can lead to gastrointestinal upset and diarrhea.
- Overfeeding or Treat Overindulgence:
- Offering excessive quantities of food or treats can overwhelm the digestive system, leading to loose stools or diarrhea in younger dogs.
Conclusion
Addressing the causes of diarrhea in puppies, including dietary factors, parasitic infections, and indiscriminate eating, requires proactive measures and vigilant care from pet owners. Recognizing the risks associated with abrupt dietary changes, parasitic infestations, and the hazards of indiscriminate eating is crucial in safeguarding the gastrointestinal health of our furry companions.
By understanding these factors and their implications, pet owners can take preventive steps such as gradual diet transitions, routine veterinary check-ups, and providing a safe environment to mitigate the risk of diarrhea in younger dogs.
Also, If your puppy is older than 12 weeks old, you can administer Dr. Smith’s probiotic/digestive enzyme soft chew, PET | TAO Harmonize GI to prevent diarrhea. You can purchase Harmonize GI online or at our clinic.
Dr. Smith co-founded PET | TAO Holistic Pet Products. PET | TAO is a harmonious combination of his expertise in veterinary medicine and Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine (TCVM).
 Timely veterinary intervention, proper diagnosis, and appropriate treatment are vital in managing diarrhea in puppies caused by these factors, ensuring the well-being and health of our younger canine friends.
Timely veterinary intervention, proper diagnosis, and appropriate treatment are vital in managing diarrhea in puppies caused by these factors, ensuring the well-being and health of our younger canine friends.
Through responsible pet care, consistent monitoring, and prompt action, you can minimize the occurrence of diarrhea in puppies, promote their overall health, and ensure a happy and comfortable life.
If you think your puppy is suffering from canine diarrhea, contact Dr. Smith for a telemedicine or in-person consultation.
People Also Ask
- My puppy has diarrhea. What should I do? If your puppy experiences diarrhea, it’s essential to monitor their condition closely. Provide access to water to prevent dehydration and temporarily withhold food for 12-24 hours. If the diarrhea persists or worsens, or if your puppy displays other concerning symptoms like lethargy or blood in the stool, contact our clinic for an appointment promptly.
- Can dietary changes cause diarrhea in young dogs? Yes, abrupt changes in a young dog’s diet can disrupt their digestive system, leading to diarrhea. Gradual transitions between foods and ensuring a balanced diet can help prevent digestive upset.
- How do I prevent my young dog’s indiscriminate eating? Training and supervision play crucial roles. Providing mental and physical stimulation, using deterrents for hazardous items, and teaching commands like “leave it” can discourage indiscriminate eating. Keeping potential hazards out of reach and ensuring a safe environment further helps prevent this behavior. Regular exercise and interactive playtime can also curb boredom-related tendencies. If the behavior persists, consult a professional trainer or behaviorist for guidance.








