Tibial tuberosity advancement surgery or TTA
is the latest surgical treatment for cranial cruciate ligament disease in the dog.
TTA is indicated for dogs weighing more than 50 lbs.
Along with TPLO, TTA is considered a “bone cutting” procedure that minimizes tibial thrust and aids in stabilizing the stifle joint.
Currently, four surgical options exist for a torn cruciate ligament in the dog. They are TPLO, TTA, Tightrope, and lateral suture.
What Is Tibial Tuberosity Advancement Surgery?
Tibial Tuberosity Advancement (TTA) surgery is a procedure primarily performed on dogs to address certain types of knee joint issues, particularly cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) injuries, which are common in canines. The CCL is equivalent to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) in humans.
When a dog’s CCL is injured or ruptured, it can lead to instability, lameness, and pain in the affected leg. TTA surgery aims to stabilize the knee joint and restore normal function by altering the biomechanics of the joint.
During a TTA procedure:
- Bone Cutting and Repositioning: A specialized surgical technique involves creating a cut in the front portion of the tibia (shin bone) where the patellar ligament inserts. The tibial tuberosity, a bony prominence, is then repositioned and stabilized using specific implants or plates.
- Change in Mechanical Forces: The repositioning of the tibial tuberosity changes the forces acting on the knee joint, reducing the stress placed on the damaged CCL. This helps to stabilize the knee during movement.
- Promotion of Healing: By altering the joint mechanics, the surgery aims to promote the healing process and enable the dog to use the affected leg more comfortably and effectively.
TTA surgery is considered an advancement in orthopedic procedures for CCL injuries in dogs. It differs from other surgical approaches, such as the traditional extracapsular repair or the TPLO (Tibial Plateau Leveling Osteotomy), by focusing on altering the angle of the patellar ligament and the tibial plateau, aiming to restore stability to the knee joint in a different way.
Post-surgery, rehabilitation and controlled exercise are crucial for successful recovery. Physical therapy and a gradual return to normal activities are often recommended to help the dog regain strength and mobility in the affected limb.
As with any surgical procedure, TTA surgery requires careful evaluation your veterinarian and/or surgeon to determine its suitability for the individual dog based on the severity of the injury, size, age, and overall health status.
Regular follow-ups and adherence to the veterinarian’s post-operative care instructions are vital for a successful outcome.
Pros of Tibial Tuberosity Advancement Surgery
One of the key advantages of TTA surgery lies in its ability to create a specific 90-degree angle between the tibial plateau and the patellar ligament within the knee joint.
This alteration effectively eliminates a biomechanical issue known as tibial thrust, a force contributing to instability, and helps address lameness issues commonly associated with certain knee joint conditions in dogs.
By restructuring this angle, TTA surgery aims to restore stability to the knee joint, facilitating smoother and more comfortable movement for the dog.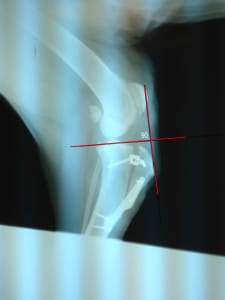
The unique structural adjustment achieved through TTA surgery often results in an early return to function for the affected limb.
The early return is coupled with reduced loss of muscle mass compared to some other surgical methods.
This can be particularly beneficial in aiding the dog’s recovery process, allowing them to regain mobility and strength in the affected leg more swiftly.
Moreover, when considering larger dog breeds, TTA surgery tends to yield better outcomes compared to alternative procedures, notably the lateral suture technique.
Large dogs, due to their size and weight, experience increased stresses on their knee joints.
TTA surgery has shown more favorable results in managing these cases, offering improved joint stability and enhanced overall function for larger breeds.
It’s important to note that the success of TTA surgery depends on various factors such as the dog’s specific condition, size, and individual health status.
I assess these factors thoroughly to determine the most suitable treatment plan for each case, often considering TTA surgery as a preferred option for certain knee joint issues in dogs, especially those involving larger breeds.
Cons of Tibial Tuberosity Advancement Surgery
One aspect to consider in TTA surgery involves the use of a bone cutter during the procedure.
This surgical technique requires precise cutting of the tibia bone, which may pose a potential risk for more severe complications compared to some other surgical methods.
There’s a chance of issues like delayed bone healing, misalignment, or even fractures at the surgical site if the procedure isn’t executed precisely or in cases where the bone quality is compromised.
The complexity of altering the bone’s anatomy can also contribute to longer recovery times and potentially raise the risk of post-operative complications such as infections or issues with implants.
However, careful pre-operative assessments and attentive post-operative care are crucial in minimizing these concerns.
I carefully evaluate the potential risks against the benefits on a case-by-case basis, taking into account the dog’s health, age, size, and severity of the knee joint issue before determining the most suitable treatment approach.
When considering the cost aspect, TTA surgery typically falls within a comparable range to procedures like TPLO (Tibial Plateau Leveling Osteotomy) and Tightrope techniques.
However, it’s essential to note that the cost of TTA tends to be higher than that of the lateral suture method.
The specific expenses associated with TTA surgery vary and depend on various factors and individual case requirements.
I always discuss the costs involved in the surgery during the initial consultations, providing detailed information to help you make informed decisions regarding your pet’s care.
Expectations of Tibial Tuberosity Advancement Surgery
After surgery, expect swelling. Most dogs have swelling starting from just above the knee down into the foot. This swelling will begin to subside after the seventh day postoperatively. As the swelling goes away, the pain soon follows.
By day twelve, most dogs are bearing weight, approximately 50%.
Increased weight bearing comes with time and most dogs return to full weight-bearing by six weeks.
It is extremely important to restrict full exercise and use of the leg until 8 weeks. The bone has been cut and it takes at least 6 weeks and up to 8 weeks for the bone to completely heal.
Do the physical therapy exercises diligently. These exercises make a huge difference in the success of the procedure!
The video below shows one of our patients walking in the clinic 14 days after TTA surgery.
The video below shows a prior TTA surgery dog running. Can you tell which leg had the TTA surgery?
LEARN MORE ABOUT DOG KNEE & LIGAMENT INJURIES AND HOW TO HELP YOUR DOG – FREE DOWNLOAD